Back muscles, the foundation of our posture and movement, are an intricate network of muscle groups that play a crucial role in our overall health and fitness. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy, physiology, and care of back muscles, empowering you with the knowledge to build strength, prevent injuries, and optimize your physical performance.
Regular exercise is widely regarded as the most effective way to prevent flexibility issues. Research suggests that engaging in physical activities helps improve range of motion, reduce muscle stiffness, and maintain joint health. Additionally, regular exercise can strengthen muscles and connective tissues, which further supports flexibility and overall physical well-being.
From the major muscle groups that comprise the back to the physiological adaptations that occur in response to exercise, this guide provides a detailed exploration of the science behind back muscle development. Discover the exercises that effectively target different muscle groups, the nutritional strategies that support growth, and the recovery techniques that promote regeneration.
If you’re experiencing lower back pain, certain exercises can provide relief. Stretching exercises , such as the knee-to-chest stretch and pelvic tilt, can help improve flexibility and reduce tension in the lower back muscles. Strengthening exercises, such as bridges and planks, can also help stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
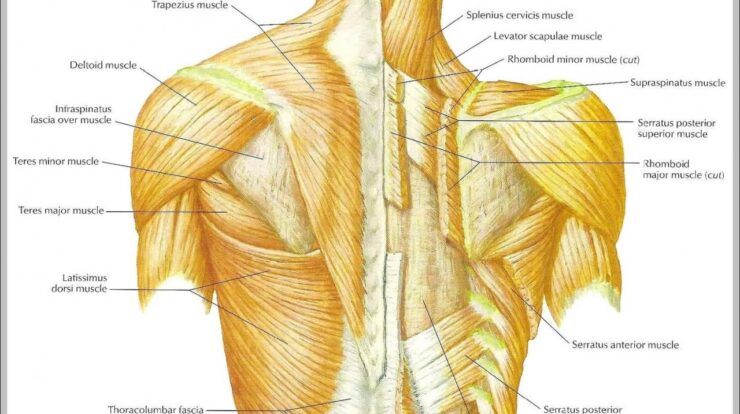
Back Muscle Anatomy
The back muscles are a complex group of muscles that play a vital role in posture, movement, and support. They are divided into two main groups: the superficial muscles and the deep muscles.The superficial muscles are located on the surface of the back and are responsible for the primary movements of the back, such as extension, flexion, and rotation.
Stiff and tight muscles can be a major contributor to back pain. When muscles are inflexible , they can put strain on the spine and surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort and pain. Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve muscle flexibility and reduce back pain.
The deep muscles are located beneath the superficial muscles and are responsible for more specialized movements, such as spinal stabilization and rib cage expansion.The major muscle groups of the back include:
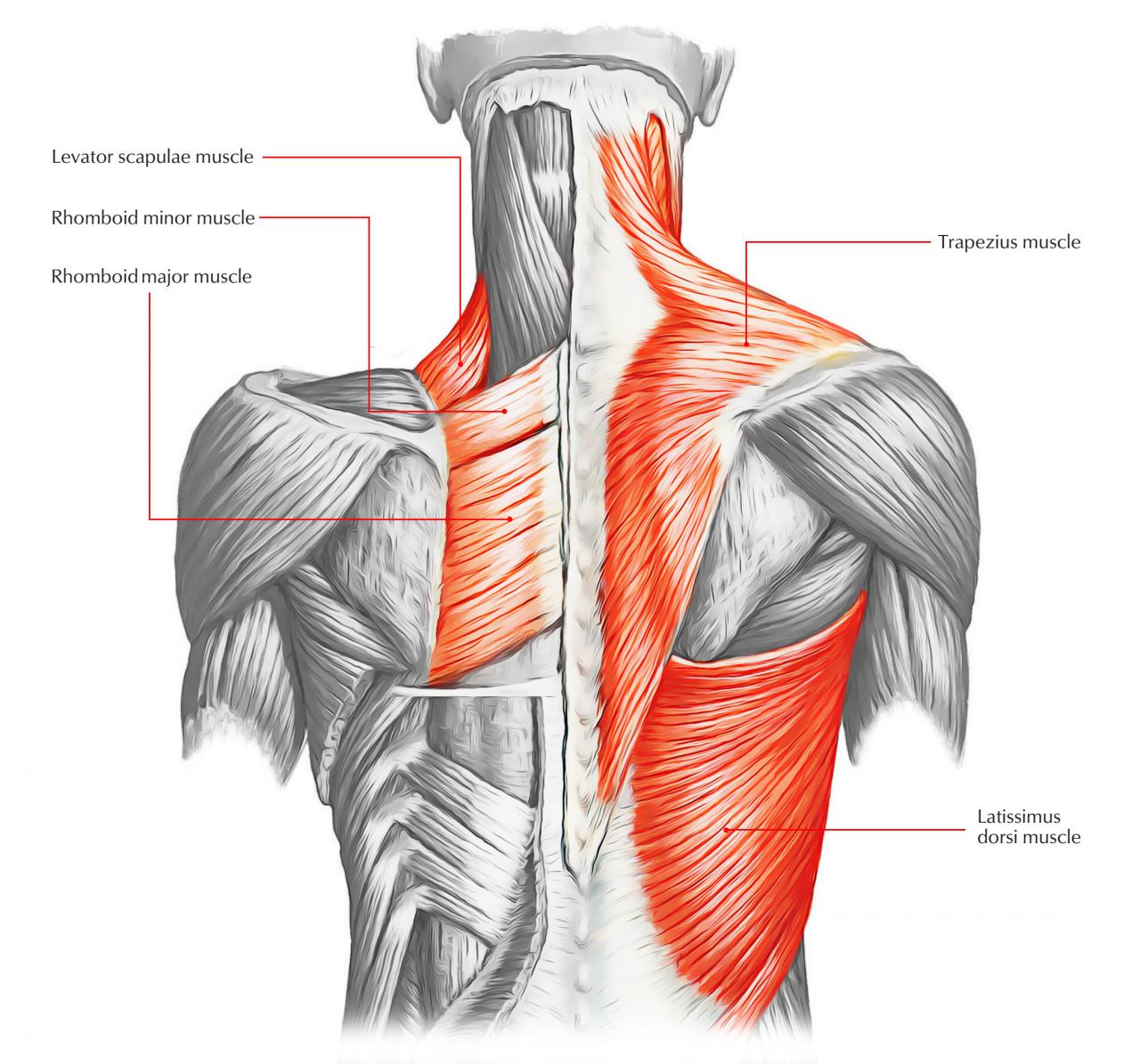
- Trapezius: Extends and rotates the neck and shoulders
- Latissimus dorsi: Extends, adducts, and internally rotates the arm
- Rhomboids: Retract and elevate the scapula
- Erector spinae: Extends the spine
- Multifidus: Rotates and stabilizes the spine
- Rotatores: Rotates the spine
Innervation of Back Muscles
The back muscles are innervated by several nerves, including:
- Dorsal scapular nerve
- Long thoracic nerve
- Thoracodorsal nerve
- Subcostal nerve
Exercises for Back Muscles
There are a wide variety of exercises that can be used to target the back muscles. These exercises can be divided into two main categories:
- Vertical pulling exercises: These exercises involve pulling a weight down towards the body, such as pull-ups, chin-ups, and rows.
- Horizontal pulling exercises: These exercises involve pulling a weight towards the body while lying down, such as barbell rows and dumbbell rows.
Vertical Pulling Exercises
- Pull-ups: A compound exercise that targets the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and biceps.
- Chin-ups: A variation of the pull-up that targets the biceps more than the latissimus dorsi.
- Rows: A compound exercise that targets the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboids.
Horizontal Pulling Exercises
- Barbell rows: A compound exercise that targets the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboids.
- Dumbbell rows: A variation of the barbell row that can be performed with one or two dumbbells.
- Seated rows: A variation of the barbell row that can be performed on a seated row machine.
Back Muscle Physiology
The back muscles, like all other muscles in the body, undergo physiological adaptations in response to exercise. These adaptations include:
- Hypertrophy: An increase in muscle size
- Hyperplasia: An increase in the number of muscle fibers
- Neuromuscular adaptations: Changes in the nervous system that improve muscle function
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the primary mechanism by which back muscles increase in size. This process occurs when the muscle is subjected to repeated bouts of resistance exercise. As the muscle is damaged, it repairs itself and becomes stronger and larger.
Lower back pain is a common issue that can be effectively addressed with the right exercises. Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. By incorporating exercises into your daily routine, you can alleviate lower back pain and improve your overall well-being.
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia is a less common adaptation, but it can occur in response to high-intensity resistance exercise. This process involves the creation of new muscle fibers.
Happy Mother’s Day to all the amazing moms out there! Your love, care, and sacrifices are truly invaluable. We appreciate you every day, but today we especially celebrate your unwavering strength and resilience.
Neuromuscular Adaptations
Neuromuscular adaptations are changes in the nervous system that improve muscle function. These adaptations include:
- Improved motor unit recruitment: The ability to recruit more muscle fibers during a contraction
- Increased firing rate: The ability to fire muscle fibers at a higher rate
- Enhanced synchronization: The ability to synchronize the firing of muscle fibers
Nutrition for Back Muscle Development
Optimal nutrition is essential for building back muscle mass. The following macronutrient recommendations are for individuals who are aiming to gain muscle mass:
- Protein: 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day
- Carbohydrates: 4-6 grams per kilogram of body weight per day
- Fats: 1-1.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day
In addition to macronutrients, it is also important to consume plenty of micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals. These micronutrients are essential for muscle growth and repair.
Meal Plan Example
Here is a sample meal plan for an individual who is aiming to gain back muscle mass:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with protein powder, fruit, and nuts
- Lunch: Chicken salad with brown rice and vegetables
- Dinner: Salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa
- Snacks: Protein shakes, fruit, and nuts
Supplement Suggestions
The following supplements can be beneficial for individuals who are aiming to build back muscle mass:
- Creatine: A natural substance that can improve muscle strength and power
- Beta-alanine: A natural substance that can improve muscle endurance
- Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): Essential amino acids that can help to promote muscle growth
Common Back Muscle Injuries
Back muscle injuries are common among athletes and individuals who engage in heavy lifting. The most common back muscle injuries include:
- Strains: A tear in a muscle or tendon
- Sprains: A tear in a ligament
- Herniated discs: A condition in which the soft, jelly-like center of an intervertebral disc pushes through the tough outer layer
- Sciatica: A condition in which the sciatic nerve is irritated or compressed
Symptoms of Back Muscle Injuries
The symptoms of back muscle injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of motion
- Numbness or tingling
- Weakness
Treatment of Back Muscle Injuries
The treatment of back muscle injuries depends on the severity of the injury. Some common treatment options include:
- Rest
- Ice
- Heat
- Massage
- Physical therapy
- Medication
- Surgery
Back Muscle Recovery and Regeneration
Rest and recovery are essential for back muscle growth and repair. After a workout, it is important to give your back muscles time to rest and recover. This will allow the muscles to repair themselves and grow stronger.There are a number of things you can do to promote back muscle recovery and regeneration, including:
- Get enough sleep
- Eat a healthy diet
- Stay hydrated
- Use ice or heat therapy
- Get a massage
- Do active recovery exercises
Active recovery exercises are light exercises that can help to promote blood flow to the muscles and aid in recovery. Some good active recovery exercises for the back include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Yoga
Summary

Understanding the complexities of back muscles is essential for anyone seeking to improve their posture, enhance their athletic performance, or simply maintain a healthy and active lifestyle. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of your back muscles, empowering yourself with a strong, resilient, and pain-free foundation for movement.
Commonly Asked Questions: Back Muscles
What are the most common back muscle injuries?
Strains, sprains, and herniated discs are among the most prevalent back muscle injuries.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Maintaining good posture, warming up before exercise, and using proper lifting techniques can help prevent back muscle injuries.
What is the best way to recover from a back muscle injury?
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce pain and inflammation during recovery from a back muscle injury.